Who loves online shopping? You, me and cybercriminals.🕵️♂️ Who doesn’t love the convenience of online shopping? From clothing to electronics, everything is just a click away. But along with this convenience comes a hidden threat – online fraud.
As online shopping becomes a part of our daily lives, so do the risks associated with it. Unfortunately, e-commerce fraud in India is rising as fast as the popularity of digital shopping platforms. You might think you're getting an amazing deal from a trusted website, only to realize you’ve fallen victim to a scam.
In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of e-commerce fraud, how to spot them, and effective ways to protect yourself while shopping online.
What is E-Commerce Fraud?
E-Commerce fraud is an umbrella term for any fraud related to an e-commerce platform, store, or business.
When a cybercriminal uses stolen credit card information to make a purchase in an e-commerce store, it is considered e-commerce fraud.
According to McAfee’s Global Festive Shopping Survey 2024, nearly 45% of Indian consumers, or someone they know, have fallen victim to deepfake shopping scams. Even major e-commerce platforms like Meesho have incurred significant losses, such as the ₹5.5 crore refund fraud orchestrated by a group in Surat.
Common Types of E-Commerce Fraud in India

Here’s a list of some of the most common types of e-commerce fraud in India.
1. Credit Card Fraud
What is it?
Credit Card fraud is one of the most common types of e-commerce fraud in India. In this type of E-Commerce fraud, the fraudsters get stolen credit card information and use it to make an online purchase.
How does it work?
The fraudster obtains the credit card information through hacking, purchasing stolen credit card credentials from the dark web, or using skimming devices. All these tools are used to gain unauthorized access to financial information of victims.
Also Read - How to Prevent Online Banking Frauds
2. Account Takeover Fraud
What is it?
Account Takeover Fraud (ATO) refers to a situation where the fraudster gains unauthorized access to a legitimate customer’s online account and makes purchases using that account.
How does it work?
There are various techniques such as phishing, data breaches or purchasing credentials on the dark web to gain access to the victim’s login credentials. Once they gain access to the victim’s account, they may change the shipping address, make purchases, or sell the account information to other fraudsters.
3. Refund Fraud
What is it?
Refund fraud occurs when a fraudster acts as a customer and requests a refund for a product or service they never purchased. This fraudulent activity occurs through providing fake order details or using stolen account credentials.
How does it work?
There are multiple ways this scam can take place:
- A fraudster may purchase a copied item from somewhere else and then use it to get a refund from the retailer of an E-Commerce platform. Through this way the fraudster is tricking the retailer into getting a refund for a duplicate product.
- The fraudsters can provide fake receipts or order confirmation for the product they never purchased.
- Fraudsters can also claim a refund from both the retailer and the credit card company for the same product purchase.
👉 Caught in E-Commerce Fraud? Get Expert Legal Help – Claim Your Free Consultation Today!
4. Interception Fraud
What is it?
Intercept fraud occurs when fraudsters place orders by using stolen cards with valid billing and shipping address linked to it. However, the fraudster changes the address before it reaches the real owner and takes away the product.
How does it work?
For interception fraud, fraudsters use common techniques:
- Making the e-commerce store change the shipment address by making a genuine and legitimate claim
- Contacting the delivery agent before the package arrives and reroute the package
5. Triangulation Fraud
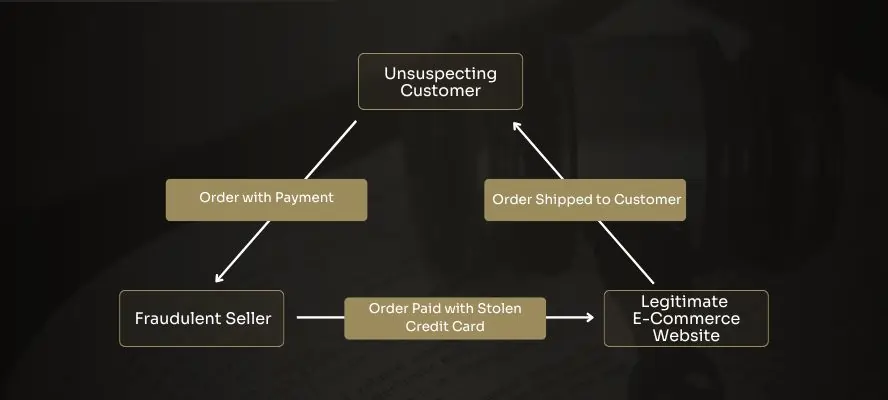
What is it?
Triangulation fraud is a more sophisticated form of phishing. In this type of fraud, a fraudster requires another shopper to launch the attack. There are three parties involved, the fraudster, a shopper and the e-commerce store.
How does it work?
The fraudster first sets up a genuine-looking website. Then they sell high-demand products at an affordable price. This is a way to attract customers. When a consumer makes a purchase and enters the credit card credentials, the fraudster will intercept the information. Fraudsters will use that information to make unauthorized purchases.
6. Dropshipping Fraud
What is it?
Currently, the dropshipping business is booming in India. A dropshipping is a form of retailing business in which the seller doesn’t keep the products they sell in stock. Instead of retailers shipping the product, the supplier and manufacturer fulfil the order as they are the ones shipping the product directly to the customer.
The dropshipping fraud occurs when a drop-shipper engages in fraudulent activities. They may try to alter the quality or availability of products, does not fulfill orders, charge extra fees, or use stolen credit card credentials to make purchases.
How does it work?
The most prominent way for a drop-shipper to commit to a fraudulent activity is by creating fake websites or social media accounts. This way they pretend to be legitimate retailers.
They take payments from customers with no intention of delivering the product. They also use fake advertising to lure customers into buying cheap quality products.
How to Identify E-Commerce Frauds
To prevent e-commerce frauds, it is important for you to identify them. Here are the most common factors through which you can identify e-commerce frauds:
- Use of Multiple Cards by One Customer: When multiple products are purchased from one account with different credit cards, it could indicate e-commerce fraud. It could very evidently be a card testing fraud.
- Different Billing and Shipping Address: Most of the time if there’s a discrepancy in billing and shipping address then it is a sign of fraud, especially in the case of interception fraud.
- Many Declined Transactions: Fraudsters may not have all the right details of the stolen credit card.
- Unusual Location: If a customer is making a purchase from an unusual location instead of their general location, this might be a fraudulent activity.
Legal Framework for E-Commerce Consumer Protection
To combat e-commerce frauds, India has a strong legal framework in place. Key laws include:
1. Information Technology Act, 2000: The IT Act, 2000 highlights consumers' protection against cybercrime threats.
Section 43A: Mandates that organizations handling sensitive personal data must implement reasonable security practices. Failure to do so, leading to wrongful loss or gain, makes the organization liable to compensate the affected person.
Section 72A: Addresses the punishment for disclosure of information in breach of lawful contract. It prescribes imprisonment for up to three years and/or a fine for individuals who disclose personal information without consent, causing wrongful loss or gain.
Section 79: Provides conditional exemption to intermediaries (e-commerce platforms) from liability for third-party information, data, or communication link made available or hosted by them. To avail this exemption, intermediaries must observe due diligence and comply with guidelines prescribed by the Central Government.
2. Consumer Protection Act, 2019: The Consumer Protection Act, 2019 contains provisions against fraudulent and misleading activities.
Section 2(7): Expands the definition of 'consumer' to include any person who buys goods or avails services through offline or online transactions, electronic means, teleshopping, direct selling, or multi-level marketing.
Section 2(47): Defines 'unfair trade practice' to include false or misleading representations concerning the quality, quantity, standard, or grade of goods or services, which is crucial in addressing fraudulent activities in e-commerce.
Section 94: Empowers the Central Government to take measures to prevent unfair trade practices in e-commerce, direct selling, and to protect the interest and rights of consumers.
👉 Know more about Laws with DigiLawyerAI - Your AI Legal Assistance
3. Consumer Protection (E-Commerce) Rules, 2020: These Rules state that E-Commerce platforms should provide accurate and correct information about the product, service or the associated vendor. This empowers customers to make informed decisions, avoiding any false claims.
Rule 4(1)(a): Requires e-commerce entities to be a company incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956 or the Companies Act, 2013, or a foreign company covered under section 2(42) of the Companies Act, 2013, or an office, branch, or agency outside India owned or controlled by a person resident in India.
Rule 5(1): States that a marketplace e-commerce entity seeking exemption from liability under Section 79 of the Information Technology Act, 2000, must comply with sub-sections (2) and (3) of that section, including the provisions of the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines) Rules, 2011.
Rule 5(3)(a): Mandates that marketplace e-commerce entities provide clear and accessible information about sellers, including their business name, whether registered or not, geographic address, customer care number, and any rating or other aggregated feedback about such seller, to enable consumers to make informed decisions
4. Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023: The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 mandates that e-commerce platforms comply with data privacy standards. This helps in managing the consumer’s information from data breaching and strengthens data security.
Section 4: Specifies that the provisions of the Act apply to the processing of digital personal data within India, including data collected online or offline and subsequently digitized.
Section 8: Outlines the rights of data principals (individuals), including the right to information about personal data processing, the right to correction and erasure, and the right to grievance redressal, thereby ensuring robust data protection for consumers engaging in e-commerce.
Top 5 Tips to Avoid E-Commerce Frauds
- Download apps only from safe and reputable sources to avoid security risks and safeguard financial transactions.
- To avoid counterfeit websites, only visit those with “https://” in the URL.
- Use safe connections and avoid unsecured public Wi-Fi to ensure safe payments.
- Regularly update software, use strong, unique passwords, and change them frequently.
- Beware of Phishing emails, calls and texts asking for financial details.
How DigiLawyer Can Help You
As the e-commerce business in India continues to grow, so does the risk of e-commerce fraud in India. From credit card fraud to refund scams, cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics, making it more important than ever for online shoppers and businesses to stay alert.
If you want to stay one step ahead of online scammers, DigiLawyer can help you navigate e-commerce fraud cases, understand your legal rights, and take action against cybercriminals.
Want More Tips and Updates? Follow Us on Instagram for the Latest Content!
- What is E-Commerce Fraud?
- Common Types of E-Commerce Fraud in India
- 1. Credit Card Fraud
- 2. Account Takeover Fraud
- 3. Refund Fraud
- 4. Interception Fraud
- 5. Triangulation Fraud
- 6. Dropshipping Fraud
- How to Identify E-Commerce Frauds
- Legal Framework for E-Commerce Consumer Protection
- Top 5 Tips to Avoid E-Commerce Frauds
- How DigiLawyer Can Help You










